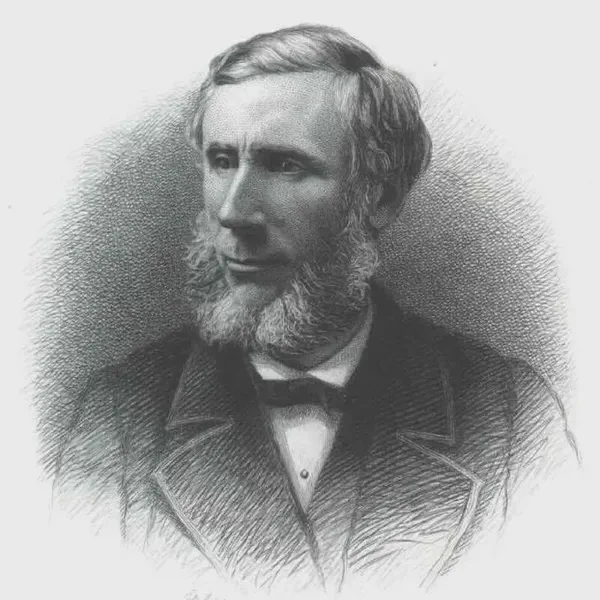
John Tyndall FRS 2 August 1820 – 4 December 1893) was a prominent 19th-century Irish physicist. Tyndall was born in Leighlinbridge, County Carlow, Ireland.
Diamagnetism
His initial scientific fame arose in the 1850s from his study of diamagnetism.
Diamagnetism is a very weak form of magnetism that is induced by a change in the orbital motion of electrons due to an applied magnetic field. This magnetism is nonpermanent and persists only in the presence of an external field.
Greenhouse Effect
Later he made discoveries in the realms of infrared radiation and the physical properties of air, proving the connection between atmospheric CO2 and what is now known as the greenhouse effect in 1859.
Why is the Sky Blue ?
The Tyndall effect is light scattering by particles in a colloid or in a very fine suspension. Also known as Tyndall scattering, it is similar to Rayleigh scattering, in that the intensity of the scattered light is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength, so blue light is scattered much more strongly than red light.
An example in everyday life is the blue color sometimes seen in the smoke emitted by motorcycles, in particular two-stroke machines where the burnt engine oil provides these particles
More From This Day